Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration (ARMD) |
'Wet' or neovascular types of ARMD
What to expect in the eye clinic Further details
|
|
Wet ARMD introduction |
ARMD is usually a progressive condition, affecting the center of the retina and the centre of the vision. . Invisible early changes occur, then usually some type of dry ARMD, such as drusen or grographic atrophy. Later, the dry changes may progress, usually slowly, to cause more atrophy and damege to the central retina. The dry changes are bascially aging, wearing out of the central retina. Then in some people, wet changes develop, with blood vessel growth and leakage in the macular area.These wet changes can be treated with anti-VEGF drugs: generally these slow down changes. The process is discussed on this page...there are many types of wet ARMD. Age-related macular degeneration is explained in more detail on other web-sites, such as the RNIB and NIH. This is an excellent animation: www.eyesight.org. Wet here. |
Contributing factors: aging, genes, diet, smoking, etc |
Age-related macular degeneration (ARMD) is one of the commonest causes of poor sight in developed countries. Whilst the causes are different in different people, certain factors may contribute. The main factor is age. |
| age | age is the main factor |
| summary | |
| smoking | contributes 32% overall, even passive smoking |
| diet | related up to ~30%; a high cholesterol from an unhealthy diet or genes Klein (2010); Toothbrushing helps. (tooth decay promotes conditions such as rheumatoid arthiritis) |
| blood pressure | high blood pressure damages the circulation...2010 target is 140 systolic
in clinic, 10 lower for diabetes. 10 lower at home. That is 120 at home
for diabetes. Best below 120 2 medications often required. |
| exercise | via blood pressure effects; regular exercise reduces risk by 70% |
| genes | ~50% is directly due to the genes we inherit, see and Gene page |
|
a high fat diet 10% (2010) |
|
| exercise | reduces progression to neovascular ARMD by 70% |
| airbourne pollution | This has been found to cause cardiovascular disease, and therefore is likely to contribute to macular disease. In urban environments, ~8% of deaths are generally attributed to pollution. More definitive proof is awaited, but may take years to obtain, especially the contribution of pollution to ARMD specifically. |
Excess alcohol is also related to ARMD, see |
|
| sunlight | Sunlight exposure, especially the summer sun, contributes to ARMD; and sunglasses protect, see. Some sunlight exposure is important...gentle sun exposure increases vitamin D production, and this will reduce the risk of many conditions such as diabetes, osteoporosis, and prostate cancer. |
| other | Other pro-inflammatory states can influence the condition, such as chlamydia High CRP, Ophthalmology 2010 |
| macular pigment | ARMD is much commoner in Caucasians...the lighter the skin or the least retinal macular pigment is related to risk. ARMD is unusual in Afro-Caribbeans, and this may be because the 'elastin' layer is thicker. Especially in wet ARMD with CNV, the elastin layer acts as a barrier to the growing CNV (new vessels). Elastin is part of Bruchs membrane link |
Other countries |
Some communities in Japan did not develop macular degeneration as people aged, but as soon as they started eating Western food the condition started to occur. Similarly, when Japanese people move to Western countries, they develop the condition more frequently. These observations suggest that the high fat (and type of fats, such as saturated and trans-fats) in our diet, the lack of protective fats (omega 3s, from fish), and salt (by increasing blood pressure) increases the number of people with ARMD. Lack of exercise as we drive everywhere in Western countries will contribute. |
|
Genes |
We inherit these from our parents. Genes are the genetic information that tells our body what chemicals to make. Overall, our genes may contribute to more than 50% of ARMD. We will soon be able to work out who is at risk...the main genes have been found. Tsee See Gene page The genes that may cause macular degeneration probably control the way used-up chemicals are removed from the eye. Being long-sighted (hyperopic) is also a risk factor |
A healthy lifestyle |
A healthy lifestyle helps to prevent
age related macular degeneration. This is important for the younger relations
of age related macular degeneration sufferers:
|
Smoking |
|
|
Blood Pressure & Exercise |
|
|
Alcohol |
| Too much may contribute indirectly by increasing blood pressure, and is related to ARMD, see. Red wine may be healthier in small amounts). Blood pressure rises after drinking (opposite...drinking 4 pints/bottle of wine). Each gram of alcohol puts systolic blood pressure up 0.24mmmHg, diastolic 0.16 mmHg. This means 1 pint of beer (2 units, each unit 8g alcohol) with 16gm of alcohol, drunk every day, will put the systolic blood pressure up (16 x 0.25=) 4mmHg. |
enlarge |
Diet |
Experts recommend a healthy diet.
Fruit/vegetables prevent 36-50% of ARMD see, see and see (fruit & vegetables lower homocysteine levels, and this improves blood flow). Pulses like beans are fine. Bread, pasta, rice and potatoes provide ‘energy’. Vegetarians have lower blood pressures and healthier lipid levels, see . A healthy diet reduces homocysteine levels, which are associated with ARMD . Certainly saturated fats increase the risk of ARMD; and fish and polyunsaturated fats halve the risk. Avoiding certain fats helps, with strong evidence here (explained more clearly here for heart disease). Nuts may help prevent ARMD (small amounts...they are fattening). |
5-9 portions of fruit/vegetables
a day, with portions of different colours The Guardian (2005) reviewed healthy diets etc, here, here , here , here and so on. See some epidemiology |
Vitamin supplements |
As the macula is the most metabolically active area in the body, with the greatest oxygen demand, it has been thought that antioxidants such as vitamins may play a critical role. The retina contains the pigments carotenoids lutein, xeaxanthin, mesoxanthin. Lutein is in darg green leaves such as kale and spinach, and most of us do not eat enough. Xeaxanthin is in orange peppers, corn, nectarines and oranges (and other yellow/orange fruits/vegetable). 'Higher dietary intake of lutein/zeaxanthin was independently associated with decreased likelihood of having neovascular AMD, geographic atrophy, and large or extensive intermediate drusen' Seddon. These vitamins are in the 'AREDS2' supplements Lack of vitamins has been linked to macular degeneration If you are unable to eat this many vegetables, AREDS2 supplements may help, but too many vitamins may be harmful. |
The AREDS1 vitamins reduce ARMD by 25%. It is not known whether or not they help patients who have a healthy diet. |
ICap (Alcon), is available in pharmacies and optometrists. This
has lutein and other vitamins in, and had been recommended by some
ophthalmologists. Beta-carotene supplements are not recommended
for smokers, as they may contribute to lung cancer. I Cap is similar
to the AREDS
vitamins that reduced ARMD risk by 28%.
zeoxanthin , Against., BMJ |
Oily fish |
| Oily fish twice a week reduces ARMD by 40%, especially oily fish such as tuna, mackerel, sardines, herring, and salmon. A Japanese diet may be helpful as above. Other omega 3 fats are helpful. See |
Cholesterol & statins |
ARMD is commoner in people with higher cholesterol levels. Atherosclerosis, caused by a high cholesterol, does contribute to ARMD, see Statin treatment reduces macular degeneration. See see,
Although statin tablets are not yet formally recommended by
all agencies, this author would recommend them for people with ARMD. Naturally all relatives of ARMD patients should address this issue of fat levels in the blood, sticking to a low fat diet with plenty of exercise, avoiding obesity, just as described on this page for ARMD patients. |
The pathology of wet ARMD |
Age-related macular degeneration (ARMD) is usually a progressive condition. It explained in more detail on other web-sites, such as the RNIB and NIH. An excellent animation: An excellent animation. Below is a brief description. Dry ARMD progresses over many years, with areas of thin retina (atrophy), and pigment changes, described here. Dry ARMD may progress to the 'wet type' (4%/year). Occasionally wet ARMD develops without any previous dry ARMD, although usually there is an area of retinal damage that triggers the process. Wet ARMD begins as new vessels growth in the macular area. This causes retinal leakage and swelling. The condition progresses to cause a scar in the macular area. If the scar is small, sight is reasonable; if large, the sight can be very poor. |
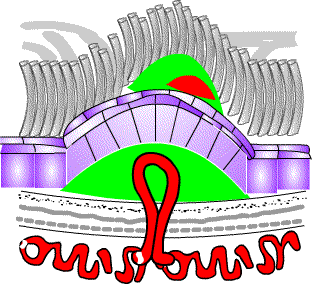
New vessels growing under the central retina in a 'classic' pattern: PDT treatment may help enlarge photos |
Wet ARMD progresses 4 times faster (a 400% increase in progression rate) in smokers. It is very difficult to predict whose dry ARMD will progress, but in addition to smoking, soft drusen, high blood pressure, smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise increase the likelihood of progression. There are several different tpes of wet ARMD. In practice most types of wet ARMD are treated the same, with Avastin (or Lucentis). Many ophthalmologists do not carry out fluorsecein anigography (it is the angiography appearance that can differentiate the different types), because the treatment is similar. |
Some types of wet ARMD
end stage |
|
|||||||||||
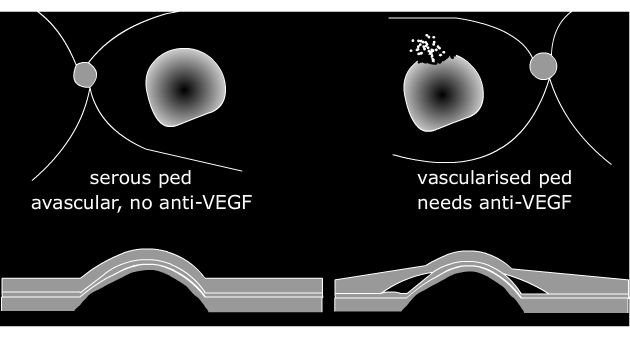
Vascularised retinal pigment epithelial detachment (PED): Occult CNV type 1 |
In a few people, the dry macular degeneration turns into this type of ARMD. Occasionally, there may have been no obvious 'dry' changes visible before this develops. In this type the damaged area looks like a dome. Fluid leaks under the retina, hence the term 'wet'. Anti-VEGF drugs are used, although is not always effective. Occasionally these drugs can cause the retina to 'rip', causing more loss of sight Eye 2011. Overall, 15% of PEDs rip, but the risk is proportional to the PED size, so a large PED is much more likely to rip. The rip typically occurs 2 months after starting Lucentis.The rip may not cause that much visual loss initially, but central vision may get worse over time. The PED will not reduce in size with treatment, but treatment will reduce intraretinal and subretinal fluid. Retina 2011 Generally ARMD with a PED is classified as 'occult' CNV, type 1. Outcomes Eye 11 Avascular PEDThere is another type of PED without any vascular element. In younger patients this is usually part of Central Serous Retinopathy. In older patients this is usually part of ARMD, and is classified as an avascular or serous ped: anti-growth factor treatment is not helpful (Eye 2010). However, if the other eye has had wet ARMD, then such as eye is at very high risk of wet ARMD itself. Eye 2012 Really (I suggest) that such eye should have regular OCT examinations, perhaps every 3 months: as yet there is no evidence to prove that this will help, but logically it will help by detecting very early disease that is much easier to treat. |
See a case. There are 3 types of PED, reviewed here (avascular, occult, polypoidal).
|
 |
||
| there is a 'PED' only, no leak | enlarge | 'PED', with a leak under the retina (shown here) or in the retina |
‘Occult’ CNV type 2 (no 'PED') |
In this type of ARMD, there are new blood vessels, but they are not clearly seen with the angiogram. ‘Occult’ CNV is the term given to a specific ‘blotchy’ appearance of the angiogram. Occult ARMD is probably an early phase of classic, see . Occult and classic patterns can occur together. Anti-VEGF drugs are used and results are generally good. The symptoms of this type of CNV are the same as 'classic CNV' . Without teatment, this type 2 occult CNV usually turns into classic CNV over the next months or years, to cause poor central vision. Large occult membranes can develop haemorrhages with anti-VEGF treatment (BJO 2008). |
|
Classic neovascular ARMD (also called ‘classic CNV’) |
|
Some dry types of macular degeneration progress to form this type of wet ARMD. It is very difficult to predict whose dry ARMD will progress, but the risk factors include those mentioned above (soft drusen, high blood pressure, smoking, poor diet, lack of exercise). When blood vessels grow under the macula, this is termed choroidal neovascularisation (CNV or CCNV). When the new vessels are seen easily on a fluorescein angiogram, they are called 'classic CNV': They look like a net of blood vessels. When a doctor looks in the retina looks elevated, there may be tiny haemorrhages, a grey area, or exudaes. This photo is a severe case. In milder cases vision may still be good. The condition may develop over days or weeks, with increasing distortion or blurred central vision. If this process is mild you can still read, but if it becomes severe reading with any magnifier is impossible. Treatment, if possible, includes the anti_VEGF drugs Avastin & Lucentis. Laser PDT may help in addition. If you notice the symptoms (central vision becoming distorted or blurred, sometimes like looking through water) you should have your eye checked with an OCT scan: see distortion.. This is usually a very serious type of macular degeneration, serious because it can cause very poor sight. It never blinds in the sense that you cannot see light and dark, but in its serious form it can damage the central vision so you can only see fingers or even the movements of hands. Once again, the side vision will normally be good, so you should always be able to walk around the house. The CNV grow at 20�/day, reaching 3000 � in 6 months.
They can be extremely difficult to see in early stages. Small membranes
gain, on average, 5 lines of vision with the Lucentis. The condition is occasionally unresponsive to treatment. Surgery/other treatment |
New vessels growing under the central retina in a 'classic' pattern: PDT treatment may help
|
|||||||||||||||
Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy |
The condition is seen as a branching choroidal network of vessels with vascular dilatation. It is more common in Chinese and Afro-Caribbeans. The choridal neovascularisation often occurs with a serous haemorrhagic PED. It is discussed in more detail here. |
|
||||||
Myopic CNV |
In this type of myopic macula disease, new vessels grow in the macula area. 5% of highly myopic eyes (more than -6.00d) develop CNV. This is similar to wet ARMD, but in myopia it may occur in much younger people. However, it is much commoner in older people with myopia. These new vessels are called 'CNV'...choroidal new vessels or choroidal neoovascularisation, as the blood vessels originate in the choroid and grow under the retina. The CNV cause retinal leakage and swelling. The condition progresses to cause a scar in the macular area. If the scar is small, sight is reasonable; if large, the sight can be very poor. The long term prognosis is not good: most eyes develop less than <6/60 vision. Younger patients have a better prognosis..the CNV get walled off. All types of wet ARMD (CNV) will progress 4 times faster in smokers, a 400% increase. In addition to smoking, high blood pressure, poor diet, lack of exercise increase the likelihood of progression and progression rate. |

New vessels growing under the central retina in myopia (similar anatomically to regular CNV) enlarge photo photo Myopic CNV Arevalo , Ruiz-Moreno, Avastin, Chan 2008 Wakabayashi 09 Some CNV are related to newly developed areas of lacquer cracks Eye 2011. |
RAP |
RAP is a 'retinal angiomatous proliferation', a type of shunt blood vessel allowing blood to flow form retina to choroid. Normally the retinal and choroidal circulation are separate. See Yannuzzi. A RAP is usually present if there is a lot of exudate and a small surface haemorrhage. RAP is not really a separate condtion, but accompanies the other types of CNV above. It is usually bilateral, but has a poor prognosis for central vision. It is common in haemorrhagic PEDs as above. 15% of RAPs close with PDT; 20% rip. Anti-VEGF and PDT reatment combined may be effective (Viola, Eye, 2010). RAPS: 33% bilateral over 3 years Eye 2010 Flap/kissing signs Retina12 |
|
Laser and anti-VEGF injection treatment |
If the choroidal new vessels (CNV) are not in the very centre of the retina, regular laser can help. (Laser is a very bright light that makes tiny burns at the back of the eye.) This appearance is called classic extra-foveal CNV. This treatment is only suitable if the CNV are well away from the fovea. Laser is not suitable near the fovea, as over the years laser burns expand and this can reduce central vision.
|
If the area of neovascular ARMD (CNV),
shown as the red area, is not under the very centre (the yellow
spot, called the fovea), and laser was used. |
|
Most people with neovascular ARMD have CNV in the centre of the retina. This appearance is called sub-foveal CNV. In general treatment will be with Avastin (or Lucentis) anti-VEGF drugs The drugs are given by injections in the eye itself about 8-12 times a year. Avastin/Lucentis usually cause regression of new vessel growth. But unfortunately, after 4 weeks, the effect of the drugs wears off, and then the new vessels start to grow again, needing repeated treatment. Such injections may be needed every month for years. Early CNV responds best, needing fewer injections. Here is an up to date treatment plan. |
CNV under the fovea |
|
Laser & other treatments for neovascular ARMD |
There are other treatments for neovascular ARMD (CNV), such as surgery, but apart from PDT laser these are not very successful and not in general use: |
|
||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
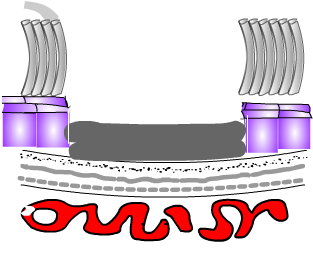
Scarring |
|
Many types of macular degeneration progress to cause scarring. 'Dry' types usually progress more slowly, but occasionally can cause very poor central vision, but this is commoner in the 'wet types'. If your conditions is severe wet scarring is likely. See a scar Even after anti-VEGF treatment for wet CNV central vision may still get worse
|
 |
|
Distortion
of vision and other symptoms:
|
|
How would you know if you have the 'neovascular' type of age related macular degeneration? Some symptoms suggest you may be developing the problem
If you do develop distortion of vision you usually need to see your ophthalmologist or have ascan at your optometrists within a few days.In the UK you may need to discuss this with your GP, or in a large city attend the Eye Emergency department. See the amsler test below. Your ophthalmologist will recommend an OCT scan, and this shows the wet ARMD immediately. In addition may recommend tests such as a fluorescein angiogram. The angiogram tells the doctor if there are new vessels, where they are, what type they are, and what type of treatment if needed. Wet ARMD progresses 4 times faster (a 400% increase in progression
rate) in smokers.
Dry ARMD may develop into 'wet' ARMD (4%/year). |
Amsler grid test |
Patients should be given the Amsler Grid test to use every day, or at least once a week, at home. These authors recommend this test, although personally I have found that patients may still present late (this is a major problem). Patients are given a grid, told to look at the central spot with their reading glassses on, using one eye at a time. If any of the adjacent lines become bent or wiggly or distorted, then CNV (blood vessels growing under the macula) may be present, and patients should see their ophthalmologist (in Birmingham attend the Eye Centre Casualty, City Hospital). The test is explained well here . A home device enabling early detection of wet ARMD Retina 2010. Unfortunately visual changes follow changes that can be detected by OCT scans BJO 2011 CNV are detected
as compared with OCT. Monthly OCTs are necessary to detect recurrences! |
Distortion of straight lines which may start to appear crooked over a few weeks usually means the ARMD is progressing. Sometimes this is due to the 'neovascular' ARMD developing, and you are advised to be checked in case laser may help. |
ARMD and the other eye |
Unfortunately age related macular degeneration can affect the other eye. See healthy lifestyle above: this may help. If you do notice a change in your sight, see distortion above. See a search . Risk from drusen. The atrophic or dry type usually does occur in both eyes, but remember this generally gets very slowly.There may be a gap of years before the wet ARMD develops in the second eye. |
What to expect in the eye clinic |
After your consultation you should be aware of the following. Ask for a second consultation if you would like one...at Good Hope a Low Vision appointment is offered and these issues are discussed a little again.
|
| The address of this site ('org' changing to 'nhs') is changing from http://www.goodhope.org.uk/departments/eyedept/ to http://www.goodhope.nhs.uk/departments/eyedept/ |
|